Effective Automation Solutions for Modern Industries: Harnessing Modern Automation Systems
- Ryan Patrick Murray
- Dec 16, 2025
- 4 min read
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, efficiency and precision are non-negotiable. Modern industries demand systems that not only streamline operations but also adapt to evolving challenges. I have witnessed firsthand how modern automation systems transform workflows, reduce errors, and boost productivity. These systems are no longer optional; they are essential for staying competitive and meeting stringent quality standards.
The Rise of Modern Automation Systems in Industry
Modern automation systems have revolutionized how industries operate. Gone are the days when manual processes dominated production lines and facility management. Today, automation integrates advanced sensors, robotics, and intelligent software to create seamless workflows.
The benefits are clear:
Increased throughput: Automated systems operate continuously without fatigue.
Enhanced accuracy: Precision controls reduce human error.
Improved safety: Dangerous tasks are delegated to machines.
Cost savings: Reduced labor and waste lower operational expenses.
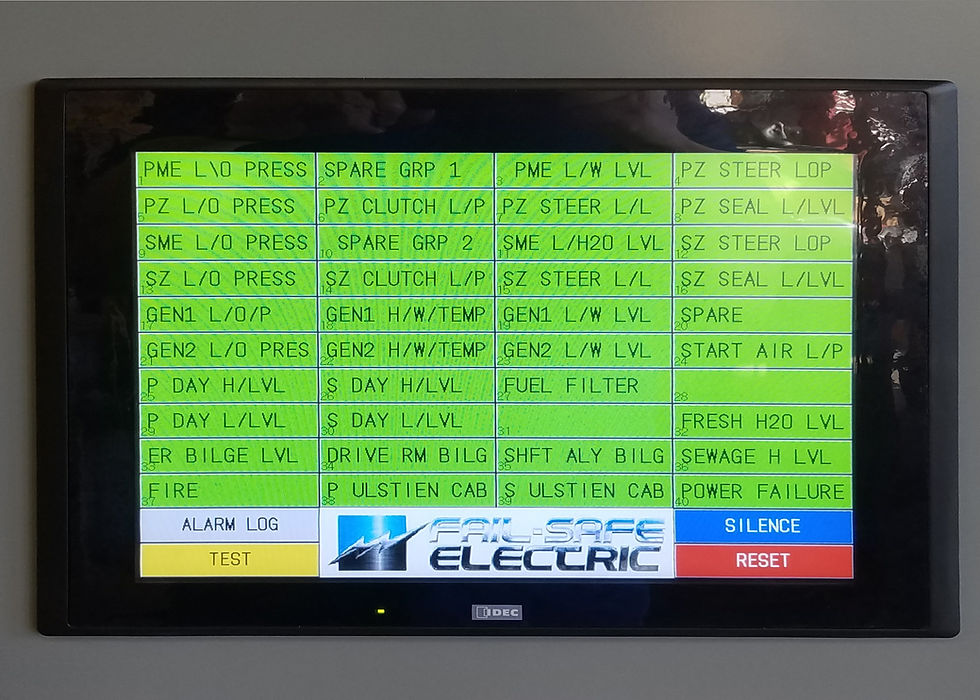
For example, in the marine industry, automated control systems monitor engine performance and environmental conditions in real time. This reduces downtime and prevents costly failures. Similarly, electrical engineers leverage programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to automate complex electrical distribution networks, ensuring stable power delivery and quick fault detection.

Modern control panels enable precise monitoring and automation in industrial settings.
Key Components of Modern Automation Systems
Understanding the building blocks of modern automation systems is crucial for effective implementation. These components work in harmony to deliver reliable and scalable solutions.
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors collect data on temperature, pressure, flow, and other critical parameters. Actuators respond by adjusting valves, motors, or switches. Together, they form the sensory and action layers of automation.
Controllers
Controllers, such as PLCs or distributed control systems (DCS), process sensor inputs and execute programmed instructions. They act as the brain of the system, making real-time decisions.
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs)
HMIs provide operators with visual dashboards and control panels. They enable monitoring, manual overrides, and system diagnostics.
Communication Networks
Reliable data exchange is vital. Industrial Ethernet, fieldbus protocols, and wireless networks connect components, ensuring synchronized operation.
Software and Analytics
Advanced software platforms analyze data trends, predict maintenance needs, and optimize processes. Integration with cloud services enhances scalability and remote access.
By combining these elements, industries achieve automation that is both robust and flexible. For instance, an electrical engineer designing a power distribution system can integrate sensors and controllers to automate load balancing and fault isolation, minimizing downtime.
What are examples of automation solutions?
Automation solutions span a wide range of applications across industries. Here are some practical examples that illustrate their impact:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in manufacturing lines automates repetitive assembly tasks, increasing speed and consistency.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) transport materials within warehouses and factories, reducing manual labor and improving logistics.
SCADA Systems (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) monitor and control large-scale industrial processes such as water treatment plants or power grids.
Predictive Maintenance Systems use sensor data and machine learning to forecast equipment failures before they occur, saving costs and preventing downtime.
Energy Management Systems optimize power consumption in facilities by automating lighting, HVAC, and machinery based on real-time demand.
In the marine sector, automation solutions include integrated bridge systems that combine navigation, engine control, and safety monitoring into a single interface. This integration enhances situational awareness and operational efficiency.

Robotic arms automate precise assembly tasks in manufacturing environments.
Implementing Automation Systems: Best Practices
Deploying modern automation systems requires careful planning and execution. Here are actionable recommendations based on industry experience:
Assess Needs Thoroughly
Identify processes that benefit most from automation. Prioritize tasks that are repetitive, hazardous, or prone to error.
Choose Scalable Technologies
Select components and software that can grow with your operations. Avoid proprietary systems that limit future upgrades.
Ensure Interoperability
Use open communication standards to integrate new automation with existing infrastructure seamlessly.
Invest in Training
Equip your team with the skills to operate and maintain automation systems. Skilled personnel maximize system uptime and effectiveness.
Plan for Cybersecurity
Protect automation networks from cyber threats by implementing firewalls, encryption, and regular security audits.
Monitor and Optimize Continuously
Use data analytics to identify bottlenecks and improve system performance over time.
For electrical engineers and facility managers, partnering with experienced automation vendors can streamline implementation and provide ongoing support. This collaboration ensures that systems meet technical requirements and comply with industry standards.
The Future of Industrial Automation Systems
Looking ahead, the evolution of modern automation systems will be shaped by emerging technologies and shifting industrial demands. Key trends include:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
These technologies will enable smarter decision-making, adaptive control, and autonomous operations.
Edge Computing
Processing data closer to the source reduces latency and enhances real-time responsiveness.
5G Connectivity
High-speed wireless networks will support massive device interconnectivity and remote monitoring.
Digital Twins
Virtual replicas of physical assets will allow simulation, testing, and optimization without disrupting actual operations.
Sustainability Focus
Automation will play a critical role in reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact.
Embracing these advancements will empower industries to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, safety, and innovation.
Modern industries cannot afford to ignore the transformative power of automation solutions. By integrating modern automation systems thoughtfully and strategically, organizations unlock new potential for growth and resilience. The future belongs to those who automate intelligently and adapt swiftly.